Write a C Program to calculates the area (floating point number with two decimal places) of a Circle given it’s radius .
Write a C program to check if a given Number is zero or Positive or Negative Using if..else statement.
Write a C program to check whether a given number (integer) is Even or Odd.
Write a C Program to find the Largest Number (integer) among Three Numbers (integers) using IF and Logical && operator.
Write a C Program to Find the Smallest Number among Three Numbers (integer values) using Nested IF-Else statement.
Write a C program to find whether a triangle can be formed or not. If not display “This Triangle is NOT possible.” If the triangle can be formed then check the triangle formed is equilateral, isosceles, scalene or a right-angled triangle.
Write a program to find the factorial of a given number using while loop.
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 5 The Factorial of 5 is : 120
Test Case 2 10 The Factorial of 10 is : 3628800
Test Case 3 7 The Factorial of 7 is : 5040
Test Case 4 11 The Factorial of 11 is : 39916800
#include<stdio.h>void main() { int n; long int fact; /* n is the number whose factorial we have to find and fact is the factorial */ scanf("%d",&n); /* The value of n is taken from test cases */ int i=1; fact = 1; while(i<=n) { fact*=i; i++; } printf("The Factorial of %d is : %ld",n,fact); }
Write a Program to find the sum of all even numbers from 1 to N where the value of N is taken as input.
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 10 Sum = 30
Test Case 2 30 Sum = 240
Test Case 3 15 Sum = 56
Test Case 4 25 Sum = 156
#include<stdio.h>void main() { int N, sum=0; scanf("%d", &N); /* The value of N is taken from the test cases */ int i; for (i = 1; i <= N; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) sum = sum + i; } printf("Sum = %d", sum); }
Write a program to find whether a given character is a Vowel or consonant. A character is taken as input.
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 C C is a consonant.
Test Case 2 o o is a vowel.
Test Case 3 I I is a vowel.
Test Case 4 k k is a consonant.
#include<stdio.h>int main() { char ch; scanf("%c",&ch); /* It reads a character from the input cases and store it in ch */ int Lower_case, Upper_case; Lower_case = (ch == 'a' || ch == 'e' || ch == 'i' || ch == 'o' || ch == 'u'); Upper_case = (ch == 'A' || ch == 'E' || ch == 'I' || ch == 'O' || ch == 'U'); if (Lower_case|| Upper_case) printf("%c is a vowel.", ch); else printf("%c is a consonant.", ch); return 0; }
Write a C program to check whether a given number (N) is a perfect number or not?
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 6 6 is a perfect number.
Test Case 2 87 87 is not a perfect number.
Test Case 3 8000 8000 is not a perfect number.
Test Case 4 8128 8128 is a perfect number.
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int N; scanf("%d",&N); /* An integer number is taken as input from test case */ int i, sum=0; for(i=1; i<N;i++) { if(N%i==0) sum+=i; } if(sum==N) printf("%d is a perfect number.",N); else printf("%d is not a perfect number.",N); }
Write a C program to count total number of digits of an Integer number (N).
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 3456 The number 3456 contains 4 digits.
Test Case 2 30000 The number 30000 contains 5 digits.
Test Case 3 57 The number 57 contains 2 digits.
Test Case 4 909 The number 909 contains 3 digits.
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int N; scanf("%d",&N); /*The number is accepted from the test case data*/ int temp, count; count=0; temp=N; while(temp>0) { count++; temp/=10; } printf("The number %d contains %d digits.",N,count); }
Write a C program to check whether the given number(N) can be expressed as Power of Two (2) or not. For example 8 can be expressed as 2^3.
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 8 8 is a number that can be expressed as power of 2.
Test Case 2 46 46 cannot be expressed as power of 2.
Test Case 3 6572 6572 cannot be expressed as power of 2.
Test Case 4 1024 1024 is a number that can be expressed as power of 2.
include<stdio.h>int main() { int N; scanf("%d",&N); /* The value of N is taken from the test case data */ int temp, flag; temp=N; flag=0; while(temp!=1) { if(temp%2!=0){ flag=1; break; } temp=temp/2; } if(flag==0) printf("%d is a number that can be expressed as power of 2.",N); else printf("%d cannot be expressed as power of 2.",N); }
Write a C program to find sum of following series where the value of N is taken as input 1+ 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 + 1/5 + .. 1/N
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 6 Sum of the series is: 2.45
Test Case 2 50 Sum of the series is: 4.50
Test Case 3 100 Sum of the series is: 5.19
Test Case 4 20 Sum of the series is: 3.60
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int N; float sum = 0.0; scanf("%d",&N); /*Read the value of N from test cases provided*/ int i; for(i=1;i<=N;i++) sum = sum + ((float)1/(float)i); printf("Sum of the series is: %.2f\n",sum); }
Write a C program to print the following Pyramid pattern upto Nth row. Where N (number of rows to be printed) is taken as input.
***** **** *** ** *
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d", &N); /*The value of N is taken as input from the test case */
int i,j;
for(i=N; i>0; i--)
{
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
{
printf("*");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
Write a C Program to find Largest Element of an Integer Array.
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 5 10 50 40 30 20 Largest element = 50
Test Case 2 7 100 50 60 70 90 30 40 Largest element = 100
Test Case 3 4 -400 -800 -700 -50 Largest element = -50
Test Case 4 7 60 70 200 12 40 -90 60 Largest element = 200
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int i, n, largest; int arr[100]; scanf("%d", &n); /*Accepts total number of elements from the test data */ for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%d", &arr[i]); /* Accepts the array element from test data */ } largest = arr[0]; for(i = 1; i < n; ++i) { if(largest < arr[i]) largest = arr[i]; } printf("Largest element = %d", largest); return 0; }
Write a C Program to print the array elements in reverse order (Not reverse sorted order. Just the last element will become first element, second last element will become second element and so on)
Sample Test Cases Input Output
Test Case 1 5 1 2 3 4 5 5 4 3 2 1
Test Case 2 4 45 65 35 25 25 35 65 45
Test Case 3 5 10 20 30 40 50 50 40 30 20 10
Test Case 4 6 41 42 43 44 45 46 46 45 44 43 42 41
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int arr[20], i, n; scanf("%d", &n); /* Accepts the number of elements in the array */ for (i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &arr[i]); /*Accepts the elements of the array */ int j, temp; j = i - 1; // last Element of the array i = 0; // first element of the array while (i < j) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; i++; j--; } for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d\n", arr[i]); // For printing the array elements } return (0); }
Write a C program to read Two One Dimensional Arrays of same data type (integer type) and merge them into another One Dimensional Array of same type.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 10 20 30 4 40 50 60 70 | 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 |
| Test Case 2 | 4 9 7 6 5 2 30 50 | 9 7 6 5 30 50 |
| Test Case 3 | 3 15 45 25 3 60 70 80 | 15 45 25 60 70 80 |
| Test Case 4 | 4 90 80 10 30 2 25 75 | 90 80 10 30 25 75 |
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int arr1[20], arr2[20], array_new[40], n1, n2, size, i; /*n1 size of first array (i.e. arr1[]), n2 size of second array(i.e. arr2[]), size is the total size of the new array (array_new[]) */ scanf("%d", &n1); //Get the size of first array from test data and store it in n1. for (i = 0; i < n1; i++) scanf("%d", &arr1[i]); //Accepts the values for first array scanf("%d", &n2); //Get the size of second array from test data and store it in n2. for (i = 0; i < n2; i++) scanf("%d", &arr2[i]); //Accepts the values for second array //Marge two arrays int j; for (i=0;i<n1;++i) array_new[i]=arr1[i]; size = n1 + n2; for(i=0, j=n1; j<size && i<n2; ++i, ++j) array_new[j] = arr2[i]; //Printing after merging for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d\n", array_new[i]); } }
Write a C Program to delete duplicate elements from an array of integers.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 50 60 30 20 30 | 50 60 30 20 |
| Test Case 2 | 6 40 20 50 30 20 10 | 40 20 50 30 10 |
| Test Case 3 | 6 50 6 7 7 2 7 | 50 6 7 2 |
| Test Case 4 | 7 2 4 2 6 4 2 4 | 2 4 6 |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int array[50], i, size; scanf("%d", &size); /*Accepts the size of array from test case data */ for (i = 0; i < size; i++) scanf("%d", &array[i]); /* Read the array elements from the test case data */ int j, k; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (j = i + 1; j < size;) { if (array[j] == array[i]) { for (k = j; k < size; k++) { array[k] = array[k + 1]; } size--; } else j++; } } for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d\n", array[i]); } }
C Program to delete an element from a specified location of an Array starting from array[0] as the 1st position, array[1] as second position and so on.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 10 20 30 40 50 4 | 10 20 30 50 |
| Test Case 2 | 6 600 500 400 300 300 200 4 | 600 500 400 300 200 |
| Test Case 3 | 4 50 60 70 80 1 | 60 70 80 |
| Test Case 4 | 5 9 10 11 1 20 5 | 9 10 11 1 |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int array[30], num, i, pos; /*num is number of elements in the array and loc is the position of the array to be deleted. starting from arr[0] as the first(1) position and so on. */ scanf("%d", &num); /*Accepts the size of array from test case data */ for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { scanf("%d", &array[i]); /* Read the array elements from the test case data */ } scanf("%d", &pos); /* Accepts the Position of the element to be deleted */ /* loop for the deletion */ while (pos < num) { array[pos - 1] = array[pos]; pos++; } num--; /* No of elements reduced by 1 as 1 element is deleted */ /* Printing the array after deletion */ for (i = 0; i < num; i++) printf("%d\n", array[i]); return (0); }
Write a C Program to Count Number of Uppercase and Lowercase Letters in a given string. The string may be a word or a sentence.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | Online NPTEL Course. | Uppercase Letters : 7 Lowercase Letters : 10 |
| Test Case 2 | National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning is a joint initiative of the IITs and IISc. | Uppercase Letters : 11 Lowercase Letters : 68 |
| Test Case 3 | Problem Solving through Programming in C. | Uppercase Letters : 4 Lowercase Letters : 31 |
| Test Case 4 | AICTE Approved FDP Course | Uppercase Letters : 10 Lowercase Letters : 12 |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int upper = 0, lower = 0; char ch[100]; scanf(" %[^\n]s", ch); /*A word or a sentence is accepted from test case data */ /* Complete the remaining part of the code to store number of uppercase letters in the variable upper and lowercase letters in variable lower. The print part of already written. You can declare any variable if necessary */ int i = 0; while (ch[i] != '\0') { if (ch[i] >= 'A' && ch[i] <= 'Z') upper++; if (ch[i] >= 'a' && ch[i] <= 'z') lower++; i++; } printf("Uppercase Letters : %d\n", upper); /*prints number of uppercase letters */ printf("Lowercase Letters : %d", lower); /*prints number of lowercase letters */ return (0); }
Write a C program to find the sum of all elements of each row of a matrix.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 3 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 | 3 6 9 |
| Test Case 2 | 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 | 6 15 |
| Test Case 3 | 3 2 4 4 5 5 6 6 | 8 10 12 |
| Test Case 4 | 3 4 1 -1 2 -2 5 -5 7 -7 8 -8 6 -6 | 0 0 0 |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int matrix[20][20]; int i,j,r,c; scanf("%d",&r); //Accepts number of rows scanf("%d",&c); //Accepts number of columns for(i=0;i< r;i++) //Accepts the matrix elements from the test case data { for(j=0;j< c;j++) { scanf("%d",&matrix[i][j]); } } int sum; for(i=0;i< r;i++) { sum=0; for(j=0;j< c;j++) { // printf("%d\t",matrix[i][j]); sum += matrix[i][j]; } printf("%d\n",sum); } }
Write a C program to find subtraction of two matrices i.e. matrix_A - matrix_B=matrix_C.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 3 2 3 5 4 5 6 6 5 7 1 5 2 2 3 4 3 3 4 | 1 -2 3 2 2 2 3 2 3 |
| Test Case 2 | 3 4 5 6 7 8 3 2 5 6 1 3 9 5 2 9 3 1 2 5 1 2 2 3 4 1 | 3 -3 4 7 1 -3 4 4 -1 0 5 4 |
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int matrix_A[20][20], matrix_B[20][20], matrix_C[20][20]; int i,j,row,col; scanf("%d",&row); //Accepts number of rows scanf("%d",&col); //Accepts number of colums /* Elements of first matrix are accepted from test data */ for(i=0; i<row; i++) { for(j=0; j<col; j++) { scanf("%d", &matrix_A[i][j]); } } /* Elements of second matrix are accepted from test data */ for(i=0; i<row; i++) { for(j=0; j<col; j++) { scanf("%d", &matrix_B[i][j]); } } /* * Subtract both matrices and store the result in matrix C */ for(i=0; i<row; i++) { for(j=0; j<col; j++) { matrix_C[i][j] = matrix_A[i][j] - matrix_B[i][j]; } } for(i=0; i<row; i++) { for(j=0; j<col; j++) { printf("%d ", matrix_C[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Write a C program to print lower triangle of a square matrix.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 | 1 0 0 1 2 0 1 2 3 |
| Test Case 2 | 4 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 | 1 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 3 3 3 0 4 4 4 4 |
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int matrix[20][20]; int i,j,r; scanf("%d", &r); //Accepts number of rows or columns for(i=0;i< r;i++) //Accepts the matrix elements from the test case data { for(j=0;j<r; j++) { scanf("%d",&matrix[i][j]); } } for(i=0; i<r; i++) { for(j=0; j<r; j++) { if(i>=j) printf("%d ", matrix[i][j]); else printf("%d ", 0); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Write a C program to print Largest and Smallest Word from a given sentence. If there are two or more words of same length then the first one is considered.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | Problem Solving through Programming in C. | Largest Word is: Programming Smallest word is: C |
| Test Case 2 | NPTEL is a joint initiative of the IITs and IISc. | Largest Word is: initiative Smallest word is: a |
| Test Case 3 | AICTE Approved FDP Course. | Largest Word is: Approved Smallest word is: FDP |
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int main() { char str[100]={0},substr[100][100]={0}; //str[100] is for storing the sentence and substr[50][50] is for storing each word. scanf("%[^\n]s", str); //Accepts the sentence from the test case data. int i=0,j=0,k=0,a,minIndex=0,maxIndex=0,max=0,min=0; char c; while(str[k]!='\0') //for splitting sentence into words { j=0; while(str[k]!=' '&&str[k]!='\0' && str[k]!='.') { substr[i][j]=str[k]; k++; j++; } substr[i][j]='\0'; i++; if(str[k]!='\0') { k++; } } int len=i; max=strlen(substr[0]); min=strlen(substr[0]); //After splitting getting length of string and finding its index having max length and index having min length for(i=0;i<len;i++) { a=strlen(substr[i]); if(a>max) { max=a; maxIndex=i; } if(a<min) { min=a; minIndex=i; } } printf("Largest Word is: %s\nSmallest word is: %s\n",substr[maxIndex],substr[minIndex]); return 0; }
Write a C Program to find GCD of 4 given numbers using recursive function
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 100 30 50 70 | The GCD is 10 |
| Test Case 2 | 49 56 147 21 | The GCD is 7 |
| Test Case 3 | 50 455 60 200 | The GCD is 5 |
| Test Case 4 | 67 89 45 41 | The GCD is 1 |
#include<stdio.h>int gcd(int, int); //You have to write this function which calculates the GCD. int main() { int a, b, c, d, result; scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a, &b, &c, &d); /* Takes 4 number as input from the test data */ result = gcd(gcd(a, b), gcd(c,d)); printf("The GCD is %d", result); } //Complete the rest of the program to calculate GCD int gcd(int x, int y) { while (x != y) { if (x > y) { return gcd(x - y, y); } else { return gcd(x, y - x); } } return x; }
Write a C Program to find power of a given number using recursion.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 2 | 5^2 is 25 |
| Test Case 2 | 10 4 | 10^4 is 10000 |
| Test Case 3 | 5 3 | 5^3 is 125 |
| Test Case 4 | 16 3 | 16^3 is 4096 |
#include<stdio.h>long power(int, int); int main() { int pow, num; long result; scanf("%d", &num); //The number taken as input from test case data scanf("%d", &pow); //The power is taken from the test case result = power(num, pow); printf("%d^%d is %ld", num, pow, result); return 0; } long power(int num, int pow) { if (pow) { return (num * power(num, pow - 1)); } return 1; }
Write a C Program to print Binary Equivalent of an Integer using Recursion.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 10 | The binary equivalent of 10 is 1010 |
| Test Case 2 | 257 | The binary equivalent of 257 is 100000001 |
| Test Case 3 | 30 | The binary equivalent of 30 is 11110 |
| Test Case 4 | 111 | The binary equivalent of 111 is 1101111 |
#include<stdio.h>int binary_conversion(int); //function to convert binary to decimal number int main() { int num, bin; //num is the decimal number and bin is the binary equivalent for the number scanf("%d", &num); //The decimal number is taken from the test case data bin = binary_conversion(num); //binary number is stored in variable bin printf("The binary equivalent of %d is %d\n", num, bin); } int binary_conversion(int num) { if (num == 0) { return 0; } else { return (num % 2) + 10 * binary_conversion(num / 2); } }
Write a C Program to reverse a given word using function.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | computer | The string after reversing is: retupmoc |
| Test Case 2 | NPTEL | The string after reversing is: LETPN |
| Test Case 3 | India | The string after reversing is: aidnI |
| Test Case 4 | Kharagpur | The string after reversing is: rupgarahK |
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h> void reverse(char[], int, int); int main() { char str1[20]; scanf("%s", str1); //The string is taken as input form the test data. int size; size = strlen(str1); reverse(str1, 0, size - 1); printf("The string after reversing is: %s", str1); return 0; } void reverse(char str1[], int index, int size) { char temp; temp = str1[index]; str1[index] = str1[size - index]; str1[size - index] = temp; if (index == size / 2) { return; } reverse(str1, index + 1, size); }
Write a C program to print a triangle of prime numbers upto given number of lines of the triangle.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 | 2 3 5 7 11 13 |
| Test Case 2 | 5 | 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47 |
| Test Case 3 | 4 | 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 |
| Test Case 4 | 6 | 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47 53 59 61 67 71 73 |
#include<stdio.h>int prime(int num); //Function to find whether the number is prime or not. int main() { int lines; scanf("%d", &lines); //Number of lines of the triangle is taken from test data. int i, j; int num = 2; for (i = 0; i < lines; i++) { for (j = 0; j <= i; j++) { while (!prime(num)) { num++; } printf("%d\t", num++); } printf("\n"); } return (0); } int prime(int num) { int i, flag; for (i = 2; i < num; i++) { if (num % i != 0) flag = 1; else { flag = 0; break; } } if (flag == 1 || num == 2) return (1); else return (0); }
Write a program to print all the locations at which a particular element(taken as input) is found in a list and also print the total number of times it occurs in the list. The location starts from 1.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 4 5 6 5 7 5 | 5 is present at location 1. 5 is present at location 3. 5 is present 2 times in the array. |
| Test Case 2 | 5 67 80 45 97 100 50 | 50 is not present in the array. |
| Test Case 3 | 7 30 50 90 30 70 30 30 30 | 30 is present at location 1. 30 is present at location 4. 30 is present at location 6. 30 is present at location 7. 30 is present 4 times in the array. |
| Test Case 4 | 4 50 60 20 10 80 | 80 is not present in the array. |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int array[100], search, n, count = 0; //"search" is the key element to search and 'n' is the total number of element of the array // "count" is to store total number of elements scanf("%d", &n); //Number of elements is taken from test case int c; for (c = 0; c < n; c++) scanf("%d", &array[c]); scanf("%d", &search); // The element to search is taken from test case for (c = 0; c < n; c++) { if (array[c] == search) { printf("%d is present at location %d.\n", search, c+1); count++; } } if (count == 0) printf("%d is not present in the array.\n", search); else printf("%d is present %d times in the array.\n", search, count); return 0; }
Write a C program to search a given element from a 1D array and display the position at which it is found by using linear search function.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 78 90 34 54 98 90 | 90 is present at location 2. |
| Test Case 2 | 6 30 40 50 20 90 60 90 | 90 is present at location 5. |
| Test Case 3 | 4 45 65 85 25 95 | 95 is not present in the array. |
| Test Case 4 | 5 6 9 5 4 7 6 | 6 is present at location 1. |
#include<stdio.h>int linear_search(int[], int, int); int main() { int array[100], search, c, n, position; /* search - element to search, c - counter, n - number of elements in array, position - The position in which the element is first found in the list. */ scanf("%d", &n); // Number of elements in the array is read from the test case data for (c = 0; c < n; c++) scanf("%d", &array[c]); //Elements of array is read from the test data scanf("%d", &search); //Element to search is read from the test case data position = linear_search(array, n, search); if (position == -1) printf("%d is not present in the array.\n", search); else printf("%d is present at location %d.\n", search, position+1); return 0; } int linear_search(int a[], int n, int find) { int c; for (c = 0 ;c < n ; c++ ) { if (a[c] == find) return c; } return -1; }
Write a C program to search a given number from a sorted 1D array and display the position at which it is found using binary search algorithm.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 10 20 30 40 50 40 | 40 found at location 4. |
| Test Case 2 | 4 44 55 66 77 10 | Not found! 10 isn't present in the list. |
| Test Case 3 | 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 | 2 found at location 2. |
| Test Case 4 | 7 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 | 100 found at location 7. |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int c, n, search, array[100]; scanf("%d",&n); //number of elements in the array for (c = 0; c < n; c++) scanf("%d",&array[c]); scanf("%d", &search); //The element to search is read from test case. int first, last, middle; first = 0; last = n - 1; middle = (first+last)/2; while (first <= last) { if (array[middle] < search) first = middle + 1; else if (array[middle] == search) { printf("%d found at location %d.\n", search, middle+1); break; } else last = middle - 1; middle = (first + last)/2; } if (first > last) printf("Not found! %d isn't present in the list.\n", search); return 0; }
Write a C program to reverse an array by swapping the elements and without using any new array.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 4 10 20 30 40 | Reversed array elements are: 40 30 20 10 |
| Test Case 2 | 5 50 60 40 30 20 | Reversed array elements are: 20 30 40 60 50 |
| Test Case 3 | 7 8 9 10 6 4 7 11 | Reversed array elements are: 11 7 4 6 10 9 8 |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int array[100], n, c; scanf("%d", &n); // n is number of elements in the array. for (c = 0; c < n; c++) { scanf("%d", &array[c]); } int temp, end; end = n - 1; for (c = 0; c < n/2; c++) { temp = array[c]; array[c] = array[end]; array[end] = temp; end--; } printf("Reversed array elements are:\n"); for (c = 0; c < n; c++) { printf("%d\n", array[c]); } return 0; }
Write a C program to marge two given sorted arrays (sorted in ascending order).
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 10 20 30 4 40 50 60 70 | Sorted array: 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 |
| Test Case 2 | 2 40 60 4 30 50 70 80 | Sorted array: 30 40 50 60 70 80 |
| Test Case 3 | 5 20 30 60 70 80 3 10 50 100 | Sorted array: 10 20 30 50 60 70 80 100 |
#include<stdio.h>void merge(int a[], int m, int b[], int n, int sorted[]); int main() { int a[100], b[100], m, n, c, sorted[200]; /* a[100] and b[100] are the two given arrays and m and n are the their respective sizes. c is a counter and sorted[200] is the final sorted array */ scanf("%d", &m); //Number of elements in the first array for (c = 0; c < m; c++) { scanf("%d", &a[c]); //Elements of first array is read } scanf("%d", &n); //Number of elements in second array for (c = 0; c < n; c++) { scanf("%d", &b[c]); //Elements of second array is read } merge(a, m, b, n, sorted); //The merged function is called where the two arrays are merged and sorted. printf("Sorted array:\n"); for (c = 0; c < m + n; c++) { printf("%d\n", sorted[c]); } return 0; } void merge(int a[], int m, int b[], int n, int sorted[]) { int i, j, k; j = k = 0; for (i = 0; i < m + n;) { if (j < m && k < n) { if (a[j] < b[k]) { sorted[i] = a[j]; j++; } else { sorted[i] = b[k]; k++; } i++; } else if (j == m) { for (; i < m + n;) { sorted[i] = b[k]; k++; i++; } } else { for (; i < m + n;) { sorted[i] = a[j]; j++; i++; } } } }
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 0.001 | Root = 1.7197 |
| Test Case 2 | 0.01 | Root = 1.7266 |
| Test Case 3 | 0.1 | Root = 1.6875 |
#include<stdio.h>float fun (float x); //Function fun returns the function value of f(x) void bisection (float *x, float a, float b, int *itr); // This function computes the root of f(x) using bisection method int main () { int itr = 0, maxmitr=10; float x, a=1.0, b=2.0, allerr, x1; // x is the value of root in each iteration, x1 is the final value of the root // a and b are the initial range for calculating the root using bisection method scanf("%f", &allerr); // allerr is the allowable error taken from test case data bisection (&x, a, b, &itr); /* Use the printf statement as given below to print the root printf("Root = %1.4f\n", x1); */ do { if (fun(a)*fun(x) < 0) b=x; else a=x; bisection (&x1, a, b, &itr); if (((x1-x)<0 -="" allerr="" x1-x="">0 && (x1-x)< allerr)) { printf("Root = %1.4f\n", x1); return 0; } x=x1; } while (itr < maxmitr); return 1; } float fun (float x) { return (2*x*x*x - 3*x - 5); } void bisection (float *x, float a, float b, int *itr) /* this function performs and prints the result of one iteration */ { *x=(a+b)/2; ++(*itr); }
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 2 | Root = 3.465754 |
| Test Case 2 | 5 | Root = 1.908690 |
| Test Case 3 | 10 | Root = 1.893289 |
| Test Case 4 | 4 | Root = 2.059000 |
#include<stdio.h>float f(float x); float df (float x); int main() { int itr, maxmitr; // itr is the iteration number and maxitr is the maximum allowable iteration float x0=1.0, x1; // x0 is the initial value and x1 is result scanf("%d", &maxmitr); // Taken from the test cases float h; for (itr=1; itr<=maxmitr; itr++) { h=f(x0)/df(x0); x1=x0-h; x0=x1; } printf("Root = %8.6f\n", x1); return 0; } float f(float x) { return x*x*x - 2*x - 3; } float df (float x) { return 3*x*x-2; }
Write a C program to sort a given 1D array using pointer in ascending order.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 20 40 50 30 10 | 10 20 30 40 50 |
| Test Case 2 | 8 90 70 30 -10 -40 20 100 50 | -40 -10 20 30 50 70 90 100 |
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a[100],i, n; scanf("%d",&n); //Number of elements of the array is taken from the test case data for (i=0; i<n; i++) { scanf("%d",a+i); // Input the array elements } int j,t; for (i=0; i<(n-1); i++) { for (j=i+1; j<n; j++) { if (*(a+i)>*(a+j)) { t=*(a+i); *(a+i)=*(a+j); *(a+j)=t; } } } // Printing sorted array in ascending order for (i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("%d\n",*(a+i)); } return 0; }
Write a C program to sort a 1D array using pointer by applying Bubble sort technique.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 6 -10 90 30 20 -100 50 | -100 -10 20 30 50 90 |
| Test Case 2 | 7 70 40 80 10 200 30 60 | 10 30 40 60 70 80 200 |
#include<stdio.h> void sort(int *a,int n); int main() { int a[20]; int n,i; scanf("%d",&n); // Enter number of elements to sort is taken from test case data for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); // The elements of the array is taken from the test data } sort(a, n); // Calling the sorting function //Printing the sorted array for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d\n",a[i]); } return 0; } void sort(int *a, int n) { int i,temp,j; for(i=1;i<n;i++) { for(j=0;j<n-i;j++) { if(*(a+j)>=*(a+j+1)) { temp = *(a+j); *(a+j)= *(a+j+1); *(a+j+1)= temp; } } } }
Write a C code to check if a 3 x 3 matrix is invertible. A matrix is not invertible if its determinant is 0.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | The given matrix is not invertible |
| Test Case 2 | 1 0 5 2 1 6 3 4 0 | The given matrix is invertible |
| Test Case 3 | 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 | The given matrix is not invertible |
| Test Case 4 | 1 2 3 0 1 4 5 6 0 | The given matrix is invertible |
#include<stdio.h>int main() { int a[3][3], i, j; long determinant; // 9 elements of matrix is taken as input from test data for(i = 0 ; i < 3; i++) for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]); determinant = a[0][0] * ((a[1][1]*a[2][2]) - (a[2][1]*a[1][2])) -a[0][1] * (a[1][0] * a[2][2] - a[2][0] * a[1][2]) + a[0][2] * (a[1][0] * a[2][1] - a[2][0] * a[1][1]); if ( determinant == 0) printf("The given matrix is not invertible"); else printf("The given matrix is invertible"); return 0; }
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 25 | The respective value of the variable v is: 56.42 |
| Test Case 2 | 16 | The respective value of the variable v is: 28.74 |
| Test Case 3 | 20 | The respective value of the variable v is: 41.62 |
<5 0="" b="b*(a-t[j]);" c="c*(t[i]-t[j]);" f="" for="" he="" i="" if="" is:="" j="" k="" of="" pre="" printf="" respective="" return="" the="" v="" value="" variable="">#include<stdio.h> int main() { float t[100]={10,15,18,22,30}, v[100]={22,26,35,48,68}; float a; //Value of the t to find the respective value of v(t) scanf("%f", &a); // This will be taken from test cases int i,j; float b, c, k =0; for(i=0; i<5; i++) { b=1; c=1; for(j=0; j<5; j++) { if(j!=i) { b=b*(a-t[j]); c=c*(t[i]-t[j]); } } k=k+((b/c)*v[i]); } printf("The respective value of the variable v is: %.2f", k); return 0; }
<5 0="" b="b*(a-t[j]);" c="c*(t[i]-t[j]);" f="" for="" he="" i="" if="" is:="" j="" k="" of="" pre="" printf="" respective="" return="" the="" v="" value="" variable="">
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 0 1 | The integral is: 0.335000 |
| Test Case 2 | 1 3 | The integral is: 8.680000 |
| Test Case 3 | -2 1 | The integral is: 3.045000 |
#include<stdio.h>
float func(float x);
int main()
{
int n=10; //Taking n=10 sub intervals
float a,b,integral; //integral is the integration result
scanf("%f",&a); // initial limit taken from test case
scanf("%f",&b); // Final limit taken from test case
int i;
float h,x, sum=0;
if(b>a)
h=(b-a)/n;
else
h=-(b-a)/n;
for(i=1;i<n;i++){
x=a+i*h;
sum=sum+func(x);
}
integral=(h/2)*(func(a)+func(b)+2*sum);
printf("The integral is: %0.6f\n",integral);
return 0;
}
float func(float x)
{
return x*x;
}
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 0.9 | y=1.4625 |
| Test Case 2 | 1.2 | y=-0.3062 |
| Test Case 3 | 0.6 | y=3.2313 |
| Test Case 4 | 1 | y=-0.3062 |
#include<stdio.h> float func(float x,float y); int main() { float xn; scanf("%f",&xn); // xn (i.e. the value of x) will be taken from test cases //Use the printf statement as: printf("y=%.4f",y); float x0=0.3,y0=5,m1,m2,m3,m4,m,y,x,h=0.3; x=x0; y=y0; while(x<xn) { m1=func(x0,y0); m2=func((x0+h/2.0),(y0+m1*h/2.0)); m3=func((x0+h/2.0),(y0+m2*h/2.0)); m4=func((x0+h),(y0+m3*h)); m=((m1+2*m2+2*m3+m4)/6); y=y+m*h; x=x+h; } printf("y=%.4f",y); // Final output return 0; } float func(float x,float y) { float m; m=(x*(x+1)-3*y*y*y)/10; return m; }
Write a C program to check whether the given input number is Prime number or not using recursion. So, the input is an integer and output should print whether the integer is prime or not. Note that you have to use recursion.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 13 | 13 is a prime number |
| Test Case 2 | 40 | 40 is not a prime number |
| Test Case 3 | 51 | 51 is not a prime number |
| Test Case 4 | 29 | 29 is a prime number |
#include<stdio.h>int checkPrime(int, int); //Function to check prime or not int main() { int num, check; scanf("%d", &num); //The number is taken from test case data check = checkPrime(num, num/2); if (check == 1) { printf("%d is a prime number\n", num); } else { printf("%d is not a prime number\n", num); } return 0; } int checkPrime(int num, int i) { if (i == 1) { return 1; } else { if (num % i == 0) { return 0; } else { return checkPrime(num, i - 1); } } }
Write a C program to reverse a word using Recursion. Input to the program is a string that is to be taken from the user and output is reverse of the input word. Note that you have to use recursion.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | KHARAGPUR | The reversed string is : RUPGARAHK |
| Test Case 2 | INDIAN | The reversed string is : NAIDNI |
| Test Case 3 | NPTELONLINE | The reversed string is : ENILNOLETPN |
#include<stdio.h>#define MAX 100 char *reverse(char[]); int main() { char str[MAX], *rev; //printf("Enter a String: "); scanf("%s", str); rev = reverse(str); //You have to write this function printf("The reversed string is : %s\n", rev); return 0; } char* reverse(char str[]) { static int i= 0; static char rev[MAX]; if (*str) { reverse(str+1); rev[i++]= *str; } return rev; }
Write a program in C to find the factorial of a given number using pointers.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 | The Factorial of 5 is : 120 |
| Test Case 2 | 10 | The Factorial of 10 is : 3628800 |
| Test Case 3 | 15 | The Factorial of 15 is : 1307674368000 |
#include<stdio.h>void findFact(int, long int*); int main() { long int fact; //factorial of the number int num1; scanf("%d",&num1); //The number is taken from test data findFact(num1, &fact); printf("The Factorial of %d is : %ld\n",num1, fact); return 0; } void findFact(int n, long int *f) { int i; *f =1; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) *f=*f*i; }
Write a C program to print the Record of the Student Merit wise Here a structure variable is defined which contains student rollno, name and score.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 3 1 Santanu 700 2 Aparna 550 3 Vivek 900 | The Merit List is : 3 Vivek 900 1 Santanu 700 2 Aparna 550 |
| Test Case 2 | 4 1 Pradip 900 2 Asutosh 600 3 Santosh 750 4 Sandip 500 | The Merit List is : 1 Pradip 900 3 Santosh 750 2 Asutosh 600 4 Sandip 500 |
#include<stdio.h> struct student { int rollno; char name[20]; int score; }; void main() { struct student s[20]; int i, n; scanf("%d" ,&n); //No. of Students taken from test data // Roll no., Name and Score of n students are taken from test data for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d", &s[i].rollno); scanf("%s", s[i].name); scanf("%d", &s[i].score); } //Complete the program so that merit list is printed in descending order struct student temp; int j; for(i=0;i<n-1;i++) { for(j=0;j<n-1;j++) { if(s[j].score<s[j+1].score) { temp=s[j]; s[j]=s[j+1]; s[j+1]=temp; } } } printf("The Merit List is :\n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d", s[i].rollno); printf(" %s", s[i].name); printf(" %d\n", s[i].score); } }
Write a C program to store n elements using Dynamic Memory Allocation - calloc() and find the Largest element
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 200 300 500 100 400 | Largest element = 500.00 |
| Test Case 2 | 6 68.90 34.79 35.86 94.98 40.06 88.70 | Largest element = 94.98 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int n; float *element; scanf("%d", &n); //Total number of elements // Allocate the memory for 'n' number of elements. //Then take the elements as input from test data element = (float*) calloc(n, sizeof(float)); if(element == NULL) { printf("Error!!! memory not allocated."); exit(0); } // Stores the number entered by the user. int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%f", element + i); } // find the largest for(i = 1; i < n; ++i) { if(*element < *(element + i)) *element = *(element + i); } printf("Largest element = %.2f", *element); return 0; }
Write a C program to add two distance given as input in feet and inches.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 40 11 10 11 | Sum of distances = 51 feet 10 inches |
| Test Case 2 | 10 5 20 5 | Sum of distances = 30 feet 10 inches |
| Test Case 3 | 5 11 9 1 | Sum of distances = 15 feet 0 inches |
#include<stdio.h> struct Distance{ int feet; int inch; }d1,d2,sum; int main() { //Enter 1st distance scanf("%d",&d1.feet); scanf("%d",&d1.inch); //Enter 2nd distance scanf("%d",&d2.feet); scanf("%d",&d2.inch); sum.feet=d1.feet+d2.feet; sum.inch=d1.inch+d2.inch; /* If inch is greater than 12, converting it to feet. */ if (sum.inch>=12) { sum.inch=sum.inch-12; ++sum.feet; } printf("Sum of distances = %d feet %d inches",sum.feet,sum.inch); return 0; }
Write a C program to find the sum of two 1D integer arrays ‘A’ and ‘B’ of same size and store the result in another array ‘C’, where the size of the array and the elements of the array are taken as input.
| Input | Output | |
| Test Case 1 | 5 10 20 30 40 50 1 2 3 4 5 | Result is 11 22 33 44 55 |
| Test Case 2 | 4 100 200 300 400 400 300 200 100 | Result is 500 500 500 500 |
| Test Case 3 | 6 15 25 35 45 55 65 5 5 5 5 5 5 | Result is 20 30 40 50 60 70 |
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void main() { int i,n; //The number of elements in each array is taken from test case data scanf("%d", &n); int *a,*b,*c; a = (int *) malloc(n*sizeof(int)); b = (int *) malloc(n*sizeof(int)); c = (int *) malloc(n*sizeof(int)); // Input Elements of First List; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",a+i); } //Input Elements of Second List; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",b+i); } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { *(c+i) = *(a+i) + *(b+i); } printf("Result is\n"); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("%d\n",*(c+i)); } }
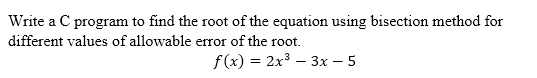










this blog very helpful for me
ReplyDeletevery helpfulll..thankss
ReplyDeleteone program is wrong .
ReplyDeleteof root program (2x cube - 3x - 5 ) .
please correct this one
r8
Deleteek kam kijiye do loop se pehle math ki header file inlude kr lijiye(#include). ar jis if me error aa rha hai us if me condition daliye if(fabs(x1-x)<allerr).fir program run karaiye.
Deleteone program some mistake bisection method program
ReplyDeletethanks
ReplyDeleteWrite a C program to print all prime number between 1 to 300 using for loop.
ReplyDeleteCode of given problem:
int main()
{
int a,b;
printf("List of prime numbers between 1 to 300:\n");
printf("%d\t",a=2);
for(a=1;a<=300;a++)
{
for(b=2;b<=a-1;b++)
if(a%b==0)
break;
else if(b==a-1)
{
printf("%d\t",a);
}
}
return 0;
}
Very informative blog!
Please take some time to visit my blog @
Top 10 programming examples in C
Thanks!